- 022-28937494 / +91 9619133576
- bhavya@bhumichem.com
Carbon Tetrachloride
Carbon Tetrachloride
Carbon Tetra Chloride -
Carbon tetra chloride, also known by many other names is an organic compound with the chemical formula CCl₄. It is a colourless liquid with a "sweet" smell that can be detected at low levels. Its Molar mass: 153.82 g/mol boiling point: 76.72 ° and density: 1.59 g/cm³.
CCl4 is a clear, non-flammable, heavy liquid that evaporates readily, producing a sweet characteristic odor similar to chloroform.
CCl4 is classified as a volatile organic compound (VOC).
Although CCl4 does not occur naturally, it is ubiquitous as a result of industrial uses. It is a stable compound, with a half-life of 6-12 months in water or soil and a half-life of 30-100 years in the atmosphere.
In the past, this compound was widely used in cleaning agents. It was also used in fire extinguishers and was known to serve as a precursor to several refrigerants. However, the use of this compound has been phased out by several governments due to its toxicity. The inhalation of large quantities of carbon tetrachloride can cause serious damage to vital organs.
Due to our honest business standards and transparent deals, we are steadily making our way to the platform of success by supplying an excellent gamut of Carbon Tetra chloride (CTC) at economical rates.
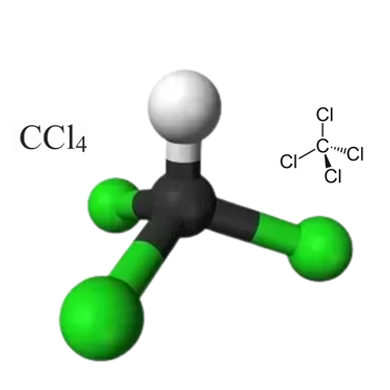
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is a manufactured chemical that does not occur naturally in the environment. Its chemical structure is shown below:
Figure 1 : Carbon tetrachloride chemical structure
It can be noted that the four chlorine atoms are positioned symmetrically at each corner around the central carbon atom in the CCl4 molecule. The bonds between the carbon atom and the chlorine atoms are covalent. As a consequence of the molecular geometry of this compound, it exhibits non-polar properties. It can be noted that the molecular structure of CCl4 is quite similar to that of CH4 (methane gas).
Properties of Carbon Tetrachloride
• Some important physical and chemical properties of CCl4 are listed below.
• The molar mass of carbon tetrachloride is 153.81 grams per mole.
• Under standard conditions, this compound exists in the liquid state. It has a colourless appearance and a sweet odour.
• The density of this compound (in its liquid state) corresponds to 1.5867 grams per cubic centimetre.
• The melting point of carbon tetrachloride is -22.93oC whereas the boiling point of this compound corresponds to 76.72oC.
• CCl4 is not very soluble in water. At a temperature of 25 degrees Celsius, the solubility of carbon tetrachloride in water is only 1 gram per litre (approx.). However, it can be noted that this compound is soluble in many organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, alcohols, ethers, and formic acid.
• Carbon tetrachloride crystallizes in a monoclinic crystal lattice.
• The coordination geometry of this compound has a tetrahedral shape. The molecular shape of this compound is also tetrahedral. It can be noted that the central atom in this scenario is the carbon atom.
• The thermal capacity or the heat capacity of carbon tetrachloride is 132.6 Joules per mole-Kelvin.
• The standard molar entropy associated with this organic compound is 214.42 Joules per mole-Kelvin.
Frequently Asked Questions on Carbon Tetrachloride
What are carbon tetrachloride uses ?
Carbon tetrachloride was commonly used in the past as a cleaning fluid (as a degreasing agent in dry cleaning institutions and other industries, and as a spot remover for clothes, furniture, and carpeting in households). Carbon tetrachloride has also been used in fire extinguishers and as a fumigant in grain in order to kill insects.
What happens when carbon tetrachloride is exposed to steam?
In the presence of metals that can behave as catalysts (such as iron and aluminium), carbon tetrachloride is decomposed by water. If it is overheated steam, carbon tetrachloride can also be decomposed to create phosgene, even without the presence of a metal catalyst.
Comment on the structure of carbon tetrachloride.
Four chlorine atoms are symmetrically arranged in the carbon tetrachloride molecule as corners in a tetrahedral structure, connected by single covalent bonds to a central carbon atom.
Why is carbon tetrachloride considered to be dangerous?
Inhalation of carbon tetrachloride by human beings often lead to negative short term effects such as nausea, vomiting, lethargy, weakness, and headaches. Oral consumption of this compound can also contribute to these symptoms. Prolonged, long-term exposure to CCl4 is known to cause acute liver damage, acute kidney damage, and damage to the central nervous system. These health hazards associated with carbon tetrachloride are the reason why it is widely regarded as a dangerous substance.
What does carbon tetrachloride smell like?
Carbon tetrachloride is known to have a strong, sweet odour. The smell associated with this chemical compound is quite similar to that of chloroform. CCl4 is a volatile organic compound that readily undergoes vaporization.